In this Blog we will learn everything about Surge Protection Devices or SPDs, also why we use it and what are the types of Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
In today’s world, we’re surrounded by electronics, whether at home, in the office, or on the factory floor. From laptops and smart TVs to PLCs and control panels, we depend on these devices every day. But all it takes is one unexpected power surge, and suddenly your equipment could be damaged beyond repair.
That’s why we have to use Surge Protection Devices (SPDs).
Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) act like silent bodyguards for your electrical system, ready to absorb excess voltage from lightning strikes, switching operations, or utility faults before it reaches your sensitive equipment. Without an SPD in place, you’re leaving your system exposed to risks that are often unpredictable and expensive to fix.
In this blog, we’ll walk through everything you need to know:
What exactly SPDs are and how they work
Why they’re critical for both residential and industrial setups
The different types of SPDs you’ll come across
And most importantly, how to choose the right one for your application
Whether you’re an engineer, a technician, or just someone trying to protect their home appliances, this guide will help you understand why surge protection isn’t a luxury, it’s a necessity.
What is a Surge Protection Device (SPD)?
A Surge Protection Device is a device designed to protect electrical devices from sudden spikes in voltage. These spikes, often caused by lightning strikes, power outages, or other electrical disturbances, can exceed the voltage ratings of your devices, causing potential damage. SPDs work by diverting excess voltage away from connected devices, thus safeguarding them from harm.

Why Surge Protection is Important
- Protects Electronic Equipment: Modern electronics, from computers and televisions to appliances and medical equipment, are sensitive to voltage changes. SPDs prevent damage to these devices, ensuring their longevity and proper functioning.
- Prevents Data Loss: For businesses and individuals alike, data is a valuable asset. A surge can corrupt or destroy important data stored on computers or servers. SPDs help avoid such losses by protecting the connected equipment.
- Minimizes Downtime: For businesses, electrical surges can result in downtime, impacting productivity and revenue. By preventing damage and ensuring that equipment remains operational, SPDs help in maintaining consistent operations.
- Enhances Safety: Electrical surges can not only damage devices but also pose safety risks, such as electrical fires. SPDs reduce these risks by managing excessive voltages.
Types of Surge Protection Devices
1. Type 1 SPDs
Description: Type 1 SPDs are designed for protection against direct lightning strikes. They are typically installed at the service entrance of a building or facility.
Application: They are used in commercial and industrial settings where direct lightning strikes are a significant concern. These SPDs are robust and can handle large surges of energy.
Features:
- High surge current capacity
- Installed on the main electrical panel
- Often include additional grounding and bonding requirements
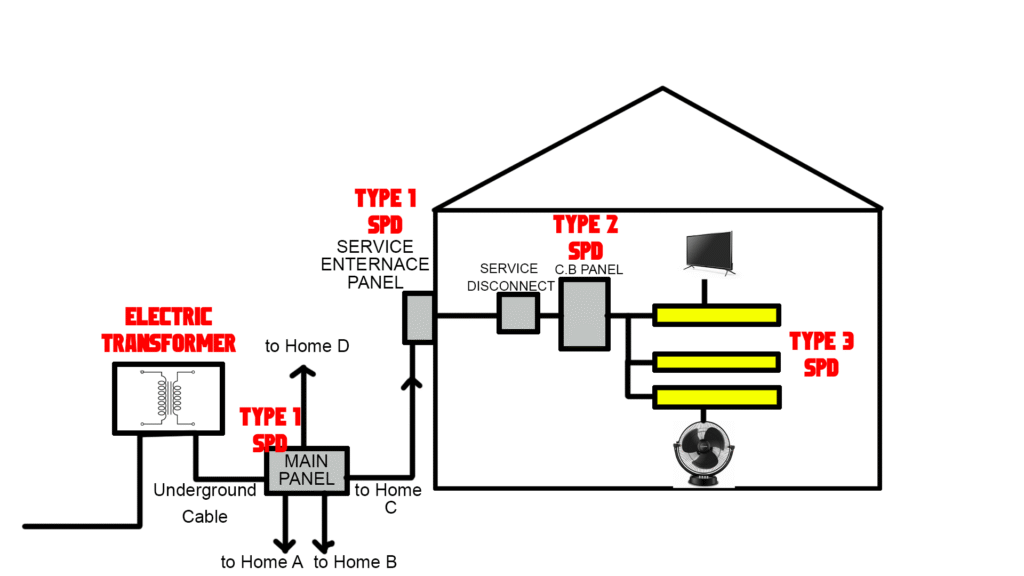
2. Type 2 SPDs
Description: Type 2 SPDs are meant to protect against electrical surges that originate from inside the building. They are installed on the distribution board or sub-panel and provide protection for electrical circuits and connected devices.
Application: Common in both residential and commercial environments, Type 2 SPDs are used to protect sensitive equipment from surges caused by switching operations or indirect lightning strikes.
Features:
- Intermediate surge current capacity
- Installed at the distribution panel
- Suitable for general-purpose protection
3. Type 3 SPDs
Description: Type 3 SPDs are designed for point-of-use protection. They are typically installed in outlets, power strips, or directly at the device to protect against smaller surges.
Application: Ideal for protecting individual devices like computers, televisions, and other electronics. They provide additional protection when used in conjunction with Type 1 and Type 2 SPDs.
Features:
- Lower surge current capacity compared to Types 1 and 2
- Installed close to the device being protected
- Often combined with filtering capabilities
4. Type 4 SPDs
Description: Type 4 SPDs are essentially component-level protection devices. They are used in conjunction with other SPDs to provide an additional layer of defense.
Application: These are typically used within devices or equipment to protect against very small surges or spikes that may still pose a risk despite having primary SPDs in place.
Features:
- Specialized for internal circuit protection
- Often integrated into electronic devices
- Provides supplementary protection
Choosing the Right SPD
Selecting the appropriate SPD depends on various factors, including the type of equipment you need to protect, the level of protection required, and your budget. Here are some tips to help you make an informed choice:
- Assess Your Needs: Determine the type and value of equipment you want to protect. For high-value or sensitive equipment, consider higher-rated SPDs.
- Consider Installation Location: Choose an SPD that suits the location where it will be installed. For comprehensive protection, a combination of Type 1, 2, and 3 SPDs might be ideal.
- Check Specifications: Look for SPDs with adequate surge current capacity (measured in kA) and response times to ensure they can handle potential surges effectively.
- Consult a Professional: If in doubt, consult with a qualified electrician or surge protection specialist to assess your needs and recommend the best solution.
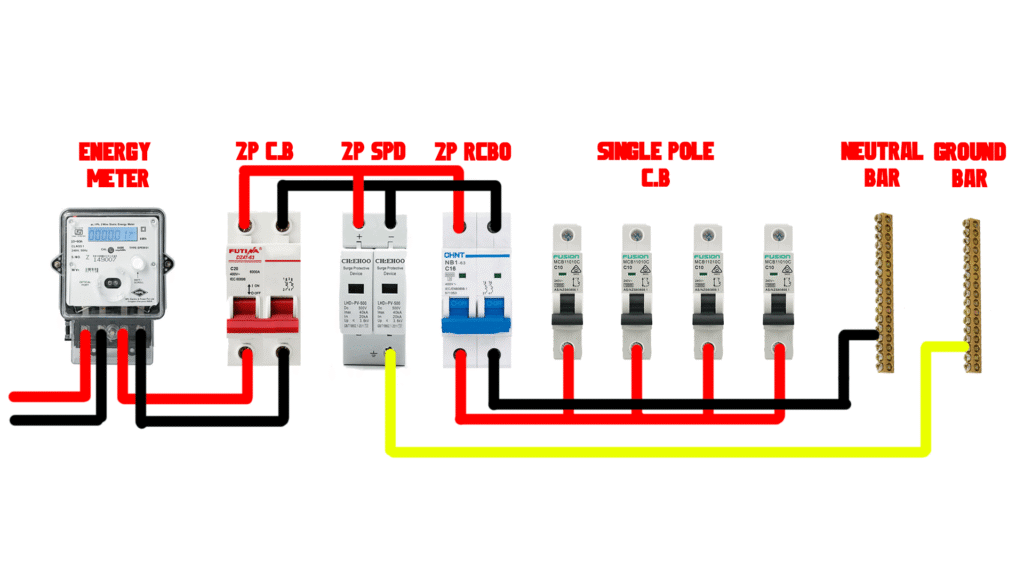
How to wire a single phase SPD
Connect the output of energy meter to the input of main breaker, connect the output of main CB to the input of earth fault breaker RCB, also connect it in parallel to the first two pins of Surge Protection Device, connect the third pin of SPD to ground bar
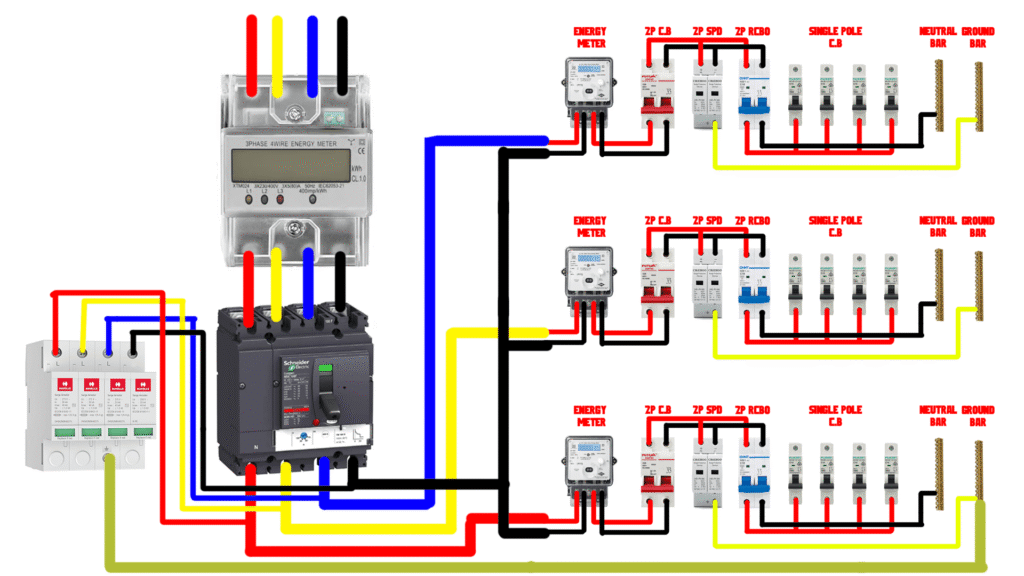
How to wire a three phase SPD
Connect the output of energy meter to the main MCCB, connect the output of MCCB to each breaker, also connect it to the first four pins of SPD, and the last pin to the ground bar
Final Thoughts
Surge Protection Devices are essential for safeguarding electronic equipment and ensuring the smooth operation of both residential and commercial electrical systems. By understanding the different types of SPDs and their applications, you can make informed decisions to protect your valuable devices from electrical surges. Whether you need protection for a single device or an entire facility, investing in the right SPD will help you avoid costly damage and maintain the integrity of your electrical systems.
