In industrial maintenance and machinery assembly, precision and efficiency aren’t just goals — they’re necessities. One tool that has quietly transformed how we install bearings is the induction heater. Whether you work in manufacturing, automotive, or aerospace, understanding this technology can make a big difference in both safety and productivity.
What Is an Induction Heater?
An induction heater is a device that uses electromagnetic energy to heat metal parts — like bearings, gears, and couplings — in a fast, safe, and controlled way. Unlike open flames or ovens, it works without direct contact and applies heat exactly where it’s needed. That makes it ideal for tasks requiring precision, like installing interference-fit components.
How Does Induction Heating Work?
The principle is simple but powerful:
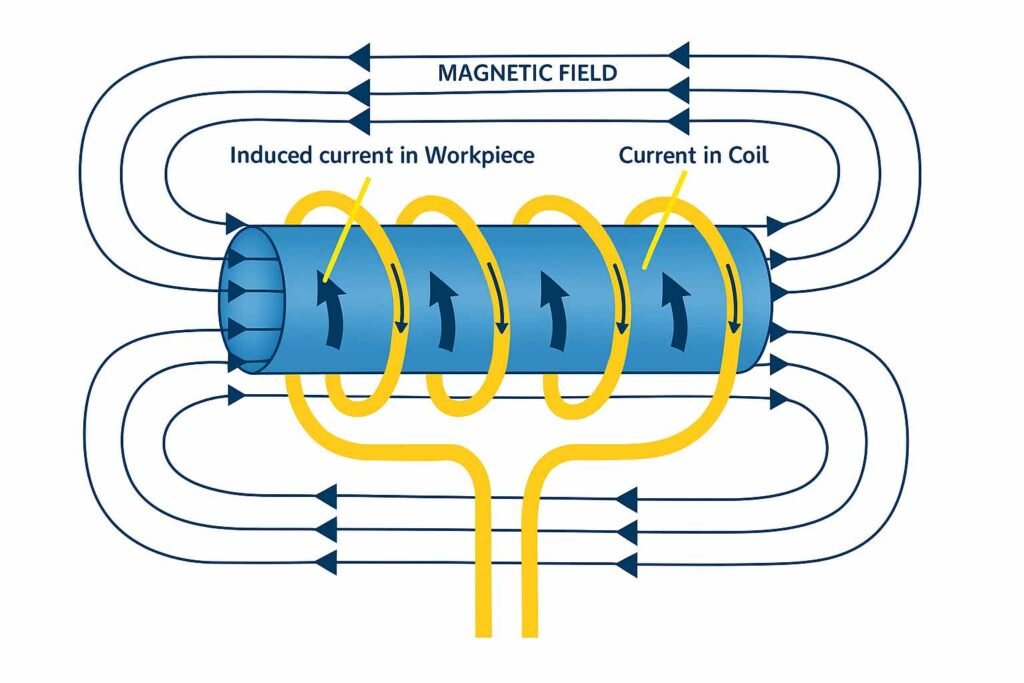
When an alternating current flows through a coil, it produces a magnetic field. Place a conductive metal part — like a bearing — inside that field, and eddy currents are generated within the metal. These currents cause resistance, which in turn heats the part from the inside out.
Because the heat is generated within the bearing itself, the process is:
- Even (no hot spots)
- Targeted (only the part gets hot)
- Clean (no flames, no contact, no contamination)
Why Use Induction Heaters for Bearings?
Here’s why so many engineers and technicians rely on induction heaters during bearing installation:
🔸 Precision You Can Control
Induction heaters allow you to set an exact temperature, ensuring the bearing expands just enough to fit the shaft or housing without overstressing the material.
🔸 Faster Heating = Less Downtime
Compared to ovens or hot oil baths, induction heaters work much faster. That means less time waiting and more time assembling.
🔸 Safety First
No open flames. No hot oils. No unnecessary risk. Induction heating keeps things safer for technicians, reducing the chance of burns or equipment damage.
🔸 Energy-Efficient
Since the heat is created directly in the part, there’s minimal energy loss. It’s a more sustainable and cost-effective way to get the job done.
🔸 Protects Bearing Integrity
Bearings are delicate precision parts. The uniform, controlled heating of induction protects them from damage and prolongs their life in the machinery.
How It’s Used in Bearing Installation
Bearings often require a tight (interference) fit onto shafts or inside housings. That’s where induction heating really shines. Here’s the basic process:
- Place the bearing on the induction heater.
- Heat it to the correct temperature (usually around 100–120°C).
- Once it’s expanded, slide it onto the shaft or into the housing.
- As it cools, it contracts and locks tightly in place — no hammering or forcing needed.
This method ensures a clean, secure fit every time, reducing the risk of damage during installation.
Final Thoughts
Induction heaters have earned their place in modern workshops and maintenance departments — and for good reason. They’re faster, safer, more precise, and more energy-efficient than traditional heating methods.
If you regularly install bearings or interference-fit components, investing in an induction heater isn’t just about making your job easier — it’s about doing it better. In the long run, it means fewer damaged parts, more uptime, and greater confidence in your installations.
