Understanding the information presented on the nameplate of a 3-phase induction motor is crucial for engineers, technicians, and anyone involved in the selection, installation, and maintenance of these motors. The nameplate provides essential details about the motor’s performance, electrical characteristics, and application suitability. In this blog, we’ll break down each element typically found on a nameplate according’s to IEC standard, using an example for clarity.
What is a Nameplate?
A nameplate is a metal or plastic label attached to a motor that contains important information about the motor’s specifications. This information helps in understanding the motor’s capabilities and limitations, ensuring it is used correctly within the intended application.
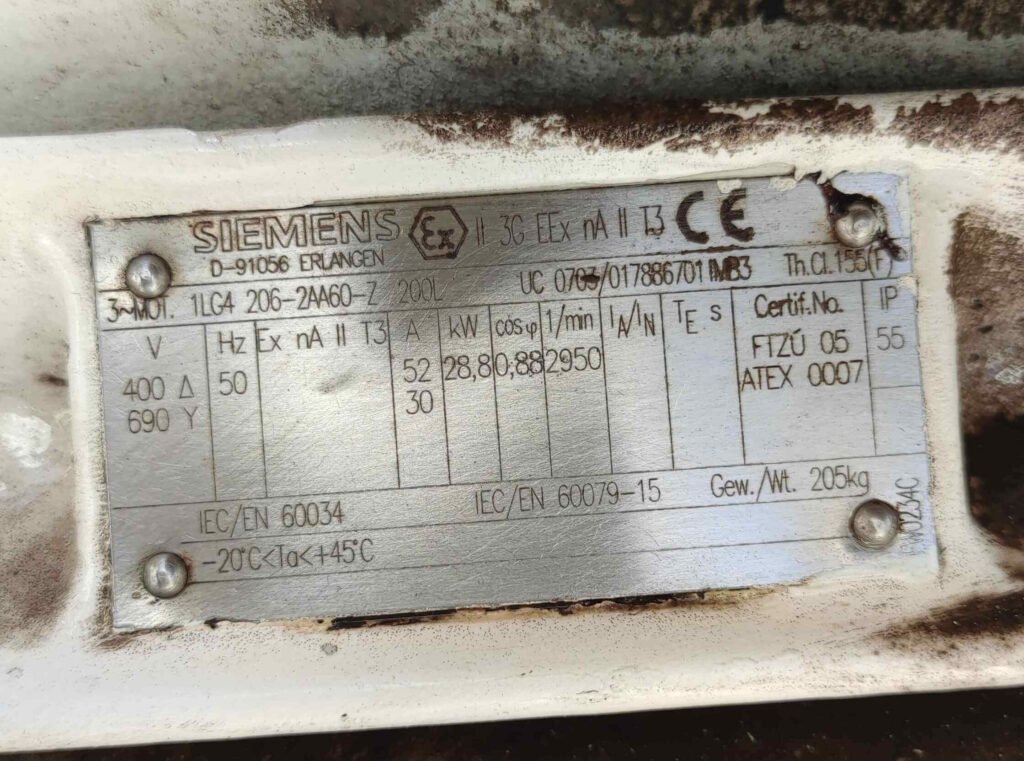
Key Elements on a Nameplate with an Example
In this section we will hit every factor in a 3 phase induction motor nameplate with the help of IEC standard with a real example
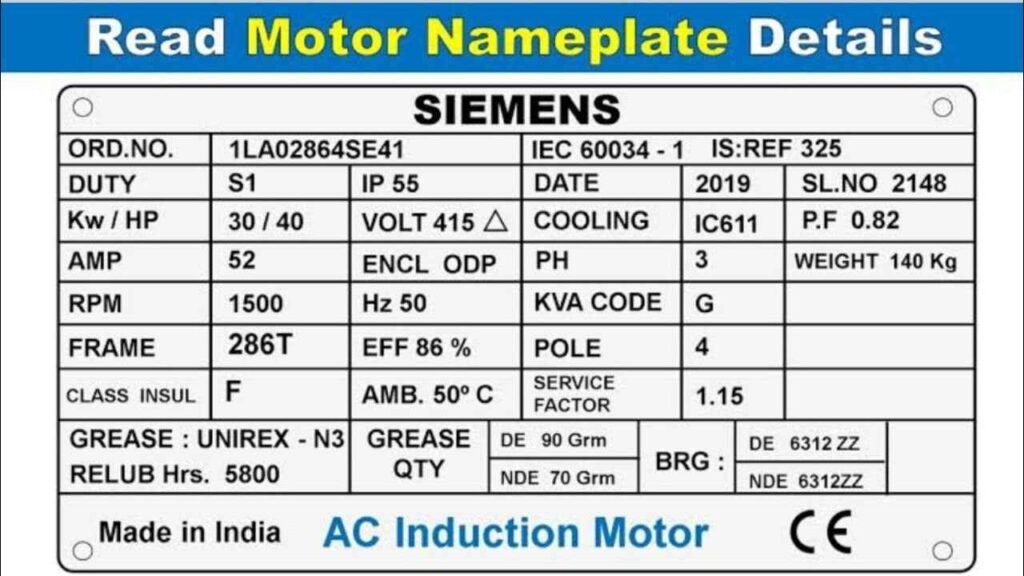
1-Manufacturer’s Name and Model Number
- Example: Siemens 1LA02864SE41
- The manufacturer’s name and model number identify the motor. The model number is particularly useful when ordering spare parts or replacements.
2-Rated Voltage
- Example: 415V
- This indicates the voltage at which the motor is designed to operate. For a 3-phase motor, you’ll often this values in IEC standard (e.g., 400V), representing delta (Δ) connection.
3-Rated Current (Amperage)
- Example: 52
- The rated current is the amount of current the motor draws at its rated voltage under full load conditions.
4-Rated Power (Output Power)
- Example: 30 kW or 40HP
- This is the mechanical power output of the motor, typically expressed in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (HP). It indicates the motor’s ability to do work.
5-Frequency
- Example: 50 Hz
- The frequency (in hertz) indicates the AC power frequency at which the motor is designed to operate. Common values are 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the region.
6-Speed (RPM)
- Example: 1500 RPM
- This is the rotational speed of the motor’s shaft when running under full load. The speed is influenced by the motor’s design and the frequency of the supply voltage.
- For 50 Hz system with 1500 RPM, this represents a 4 Poles motor.
7-Efficiency
- Example: 86%
- Efficiency indicates how well the motor converts electrical power into mechanical power. A higher efficiency means less energy is lost as heat.
8-Power Factor
- Example: 0.82
- The power factor is the ratio of real power (kW) to apparent power (kVA) and indicates the efficiency of power usage. It is crucial for understanding the motor’s load on the electrical system.
9-Service Factor
- Example: 1.15
- The service factor indicates the motor’s ability to operate above its rated power for short periods. A service factor of 1.15 means the motor can operate at 115% of its rated power.
10-Insulation Class
- Example: Class F
- This denotes the maximum temperature the motor’s insulation can withstand. Class F insulation, for example, is rated for 155°C.
11-Duty Cycle
- Example: S1 (Continuous Duty)
- The duty cycle describes the motor’s operating mode. S1 means the motor is designed for continuous operation.
12-IP Rating
- Example: IP55
- The IP (Ingress Protection) rating indicates the level of protection against dust and water. IP55 means the motor is protected against dust and low-pressure water jets.
13-Frame Size
- Example: 286T
- The frame size determines the physical dimensions of the motor, including mounting and shaft size. This is important for mechanical compatibility with the equipment.
14-Ambient Temperature and Altitude
- Example: 40°C, 1000m
- These values indicate the maximum ambient temperature and altitude at which the motor can operate without derating.
15-Bearing Type
- Example: 6312 ZZ for drive end and non drive end
- The bearing type provides information on the bearings used in the motor, which is important for maintenance and replacement.
16-Number of Poles
- Example: Four
- For 50 Hz system with 1500 RPM, this represents a 4 Poles motor.
17-Greasing Quantity
- Example: 90 gm for DE and 70 gm for NDE
- This represents amount of greasing for the two bearings every 4000 working hours.
Final Words
With the help of IEC standard reading and understanding the nameplate of a 3-phase induction motor is essential for proper installation, operation, and maintenance. By interpreting the details on the nameplate, you can ensure that the motor is suitable for your application, avoid operational issues, and extend the motor’s lifespan.
Feel free to refer back to this guide whenever you encounter a motor nameplate, and don’t hesitate to share this information with colleagues or friends who might benefit from it.
