Ever wondered why starting a three-phase motor isn’t as simple as flipping a switch?
These motors are known for their strength and reliability, that’s why they’re everywhere in the industrial world. But when it comes to starting them, things get a bit tricky. High inrush currents, mechanical stress, and system limitations can make it a challenge. In this post, I’ll walk you through the most common methods used to start 3-phase induction motors, the pros and cons of each one, and when to use which—so you’ll know exactly what works best in real-world scenarios.
Starting Methods of 3-Phase Induction Motors
1. Direct-On-Line (DOL) Starter
This is the most basic method: you apply full voltage directly to the motor terminals. It’s simple, low-cost, and works well with small motors. But it draws a huge inrush current—up to 6–8 times the rated current—which can be too much for bigger systems or weak networks.
So it’s better to use this method only with small motors or applications where the high starting current does not pose a problem. It’s commonly used in fans, small pumps, and other low-torque applications.
Advantages
- Simplicity: Requires minimal equipment and is straightforward to implement.
- Cost-Effective: The initial setup cost is low compared to other starting methods.
- Reliability: Fewer components mean fewer potential points of failure.
Disadvantages
- High Starting Current: Can draw up to 6-8 times the motor’s full-load current, which can affect the power supply and other equipment.
- Mechanical Stress: The high starting current can cause significant mechanical stress on the motor and connected load.
2. Star-Delta Starter
A very popular method in industrial setups. The motor starts in star (Y) connection (lower voltage per phase), then switches to delta (Δ) once the motor reaches to a certain speed. It reduces the starting current but needs careful timing and works best with motors that can handle a voltage drop during startup.
Advantages
- Reduced Starting Current: Current is limited to approximately one-third of the DOL starting current.
- Less Mechanical Stress: Lower starting current reduces stress on the motor and mechanical components.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Requires additional control gear and circuitry.
- Not Suitable for All Motors: Only applicable to motors designed for star-delta starting.
So it’s better to use for medium-sized motors (typically above 5.5 kW) where reducing the starting current is important. It’s commonly used in compressors, conveyors, and large fans.
3. Autotransformer Starter
If you need even more control, this method uses an autotransformer to reduce voltage during startup. It’s more expensive but provides better torque than star-delta, Autotransformer starting involves using an autotransformer to step down the voltage applied to the motor at startup. The motor is then switched to full voltage once it reaches a certain speed.
advantages
- Reduced Starting Current: The autotransformer reduces the starting voltage, which in turn reduces the starting current.
- Less Mechanical Stress: Reduces the mechanical stress on the motor and load.
Disadvantages
- Higher Cost: Requires an autotransformer and additional control equipment.
- Complexity: More complex to implement and maintain.
So it’s suitable for large motors where high starting currents need to be managed. It’s commonly used in heavy machinery, large pumps, and industrial fans.
4. Soft Starter
These use solid-state electronics to ramp up voltage gradually, reducing mechanical stress and inrush current. They’re more expensive than older methods but great for protecting gearboxes, pumps, and delicate systems.

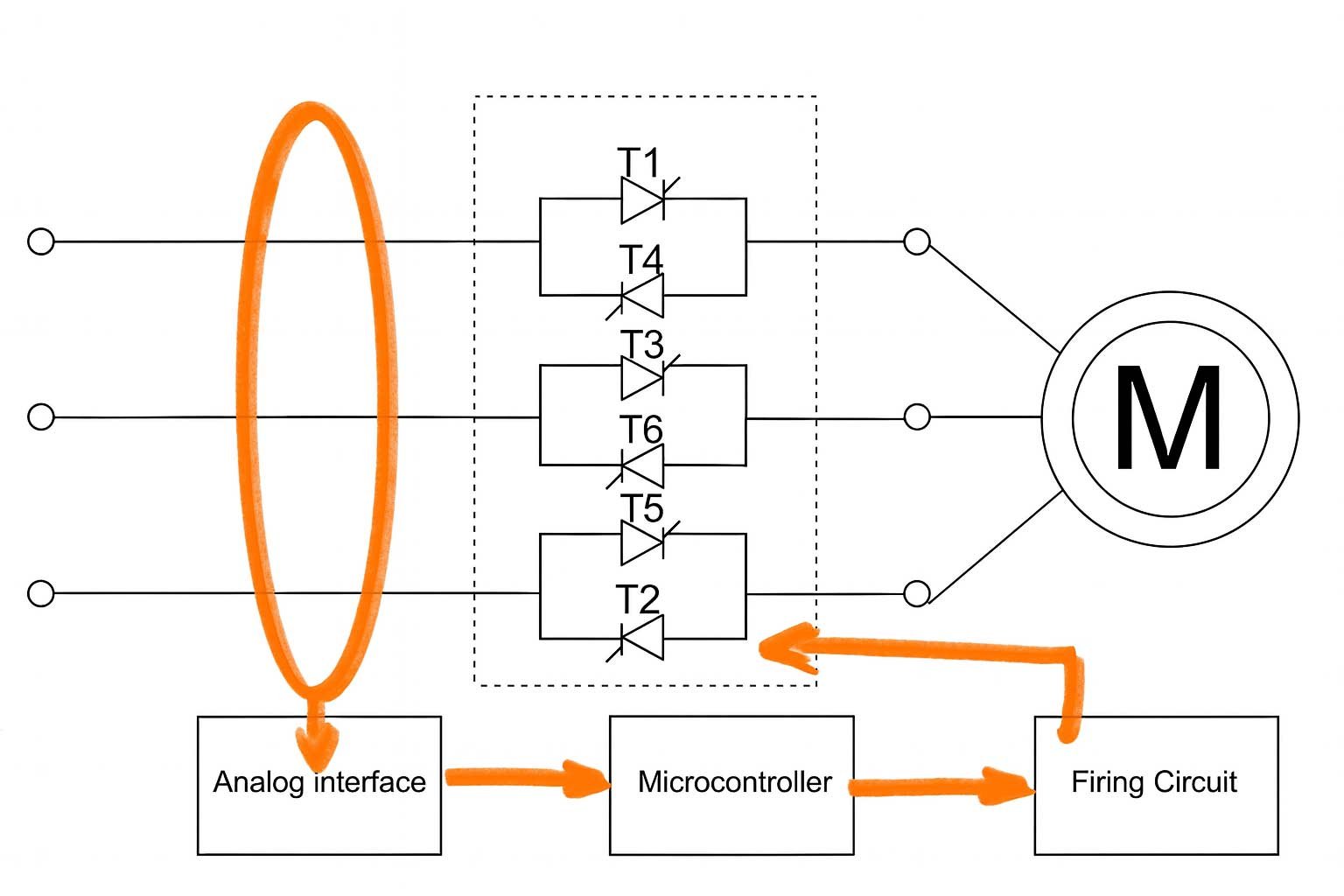
advantages
- Smooth Start: Reduces mechanical and electrical stress by providing a gradual start.
- Adjustable: Many soft starters offer adjustable ramp-up times and other features.
Disadvantages
- Cost: More expensive than DOL or star-delta starting.
- Complexity: Requires a soft starter unit, which may involve additional setup and maintenance.
So soft starter is Ideal for applications where smooth acceleration is critical, such as in conveyor systems, crushers, and mills.
5. Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)
The most advanced method. VFDs give you complete control over voltage and frequency, allowing for smooth starts, stops, and energy savings. Perfect for applications that require speed control—but keep in mind they cost more and require programming.
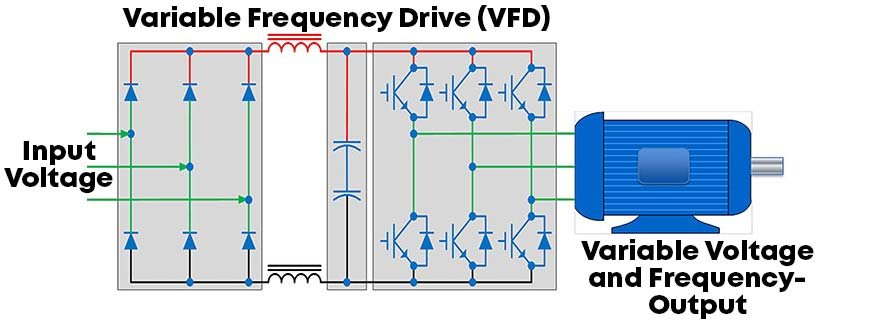
advantages
- Full Control: Provides precise control over motor speed and torque.
- Energy Efficiency: Can lead to significant energy savings by adjusting speed to match the load.
Disadvantages
- High Initial Cost: VFDs are more expensive compared to other starting methods.
- Complexity: Requires proper setup and maintenance, and might involve a steep learning curve.
So VFD is Suitable for applications requiring variable speed control, such as pumps, fans, and processing equipment. It’s also used in applications where energy efficiency is a priority.
Conclusion
Want help deciding which method suits your motor setup? Drop your case in the comments or check out our motor starter diagrams in the blog!
Choosing how to start a 3-phase induction motor isn’t a one-size-fits-all decision. It really depends on several factors—like the motor size, what the application needs, and of course, your budget.
If you’re dealing with a small motor, a Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter might be all you need—simple and cost-effective. But as motor size and system sensitivity grow, other methods like star-delta, autotransformer, or soft starters become more useful, especially when you want to cut down those heavy starting currents and reduce mechanical stress.
And if you’re looking for more control and energy savings, a VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) is hard to beat—though it does come with a higher price tag and a bit more complexity.
At the end of the day, understanding your system’s needs is the key. When you know what your motor and application require, choosing the right starting method becomes much easier—and you’ll get smoother operation and better long-term performance.
